6.2.7. Material flows (Raw materials, products, relation with process in-/outflows)¶
The mass flows into and out from different processes within the system can be correlated among themselves and with the inputs and outputs to and from the production process (raw materials, products).
For this purpose a network of mass flows can be defined:
- inflows and outflows of processes can be connected among themselves and with products and raw materials
- flows can be splitted and mixed
- quantities can be scaled by a scale factor f_c (e.g. the quantity of water to be heated in some process A is f_c times the quantity of final product P)
Step 1: Open the menu Material Flows
A graphical editor is opened in which You can see all processes and products in the system
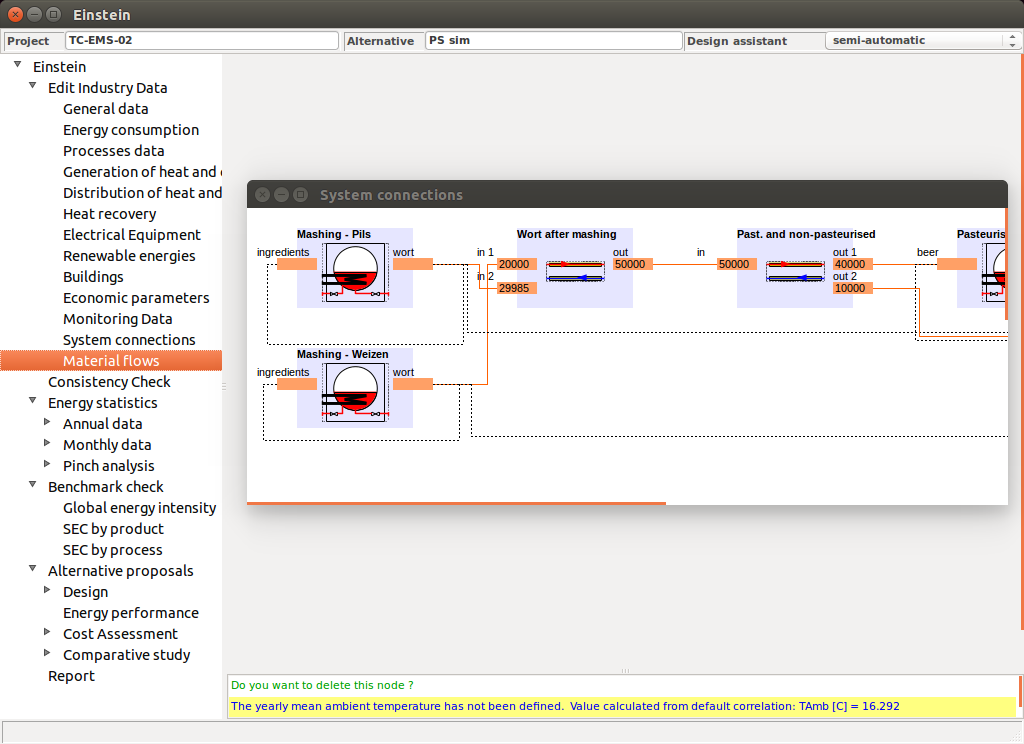
You can edit the mass flow network graphically in the following ways:
- connecting inputs and outputs by clicking first on an output and then on the connected input
- deleting connections (click on the connection and select “delete connection”)
- changing the type of connections (click on the connection and select type)
- adding splitters and mixers (right-click of the mouse on the background)
- deleting splitters or mixers (right-click of the mouse on the node)
- editing the parameters of a mixer or splitter (click on the node)
In the following the use of mixers, splitters and connection types is described in more detail:
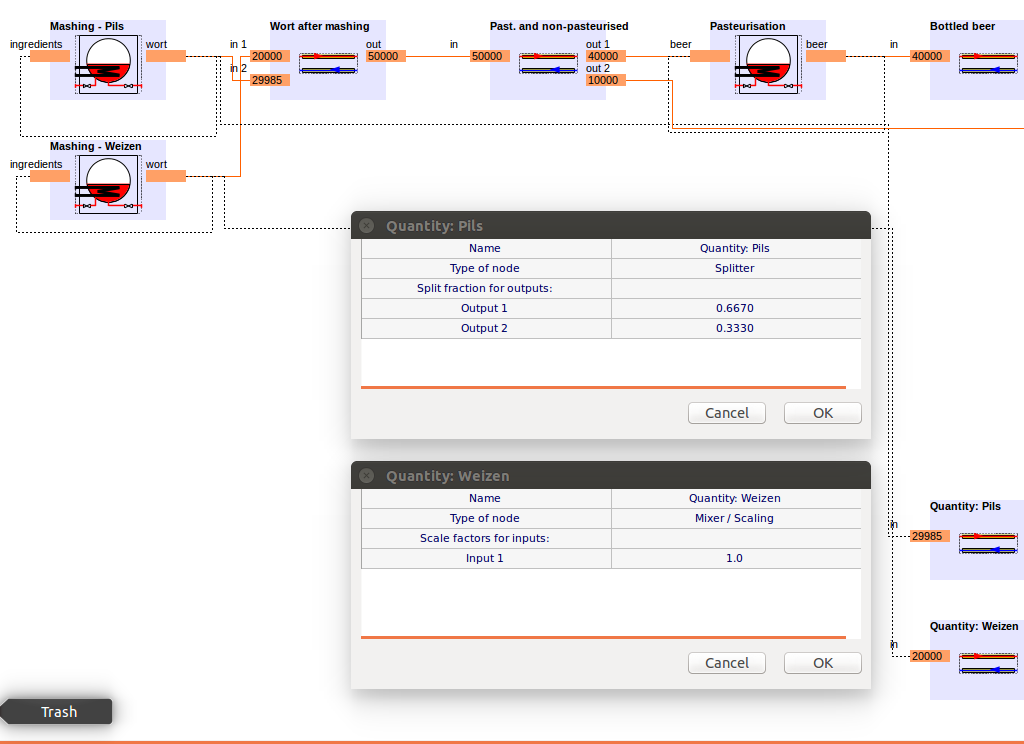
6.2.7.1. Mixers¶
Mixing nodes can be used in order to mix (sum up) the mass flows of different connections. E.g. the products processed in either process A and process B are both further processed in a third process C.
Each of the incoming flows furthermore can be scaled by a scale factor f_c [1], so that
M_out = SUM over i [ M_in(i)*f_c(i) ]
6.2.7.2. Splitters¶
Are used to split a flow into different destinations. For each branch the split fraction f_s [1] can be defined.
M_out(i) = f_s(i)*M_in
6.2.7.3. Connection Types¶
Connections can be of one of the following types:
- physical connections:
- only one physical connection can start/end and any input/output of each node (solid lines in the diagram).
- mass balances (SUM M_in = SUM M_out) are calculated based on physical connections only)
- information flow: some mass flows can be correlated, even if there is no (direct) physical connection between the corresponding nodes. In this case an information flow - type connection can be used (dashed lines in the diagram).
| [1] | (1, 2) Important Note: As with all parameters in EINSTEIN, also scale factors and split factors can, but do not have to be defined. Undefined parameters in many cases can be calculated or estimated by the consistency and completeness checking module. |